Introduction
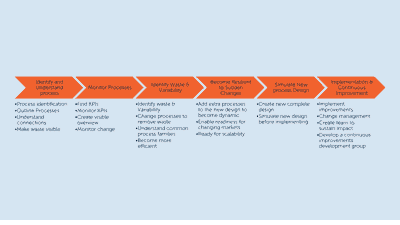
Companies of all sizes work on increasing their market share and profitability in a world with increased competition. A way to do so is to apply the Lean techniques and Six Sigma methodologies to eliminate and control waste and variability within their processes[1]. When redesigning a company’s processes, it is therefore critical to systematically impose process control to improve efficiency by reducing waste and variability[2]. This article reveals some methods on how to identify waste and variability and is a part of the six-step “road map”, which is depicted in Figure 1.
Identify Waste
This section will describe various lean techniques focused on eliminating waste from the processes. Waste (also referred to as muda – a Japanese term for waste) is defined as any activity that does not create value for the customer[3]. The first technique called TIMWOOD identifies seven types of waste which is explained in Table 1[4]. This technique are very useful to help companies identify and become aware of the waste that impacts the efficiency of their process flow.
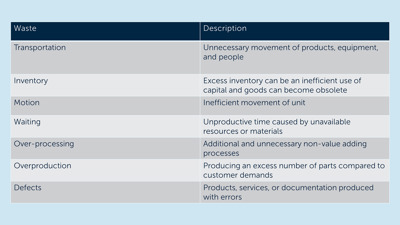
Not all categories of waste can be applied to all processes or services. But depending on the specific process or service, some of the waste types will apply.
5S Lean Principles is another widely used technique, which systematically organizes workspaces to ensure that work is performed efficiently and effectively by removing what’s unnecessary and organizing things logically. 5S follows the sequence of sorting, setting in order, shining, standardizing, and sustaining[5].
The 5-Why method helps determine the cause-effect relationship in a problem, e.g., an inefficient process flow. This method can be applied whenever the cause of the problem is not clear, where asking five whys can help solve the problem without kickstarting a resource-heavy investigation. The simple investigation tool is fulfilled by repeatedly asking the question “Why”, while you peel away layers of issues and symptoms that can lead to the root cause of the problem[6], thus helpful to find waste and variability in a process.
Lastly, Value Stream Mapping (VSM) is a common Lean technique that helps identify waste. VSM is a chart showing the flow of material and information in a supply chain and helps to capture value-added- and non-value-added activities and their respective durations. VSM therefore clearly reveals bottlenecks and where waste is generated[7].
Identify Variability
Variation consists of two categories, i.e., variability and uncertainty, where the former refers to natural variation and the latter refers to the degree of precision with which a quantity is measured[8]. Identifying and decreasing variation in a process flow is of high significance, as excess variation in processes usually results in increased costs, higher complexity, less predictability and possible decreased customer satisfaction[9].
One of the most widely known strategies and methods to improve manufacturing by removing variability in products, services and processes is Six Sigma. Six Sigma was first introduced in the early 90’s by Motorola and focuses on quality control. In another way, Six Sigma is a statistical expression that represents the standard variation also called standard deviations. Six standard deviations from the mean, are the general business benchmark, which gives a 99% efficiency level seen in Figure 2 to the left.
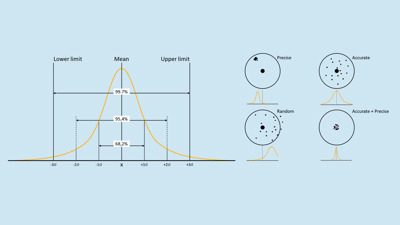
The goal is to remove variability and obtain a process that is both accurate and precise as seen in Figure 2 to the right. A process can have little variation and thereby be precise. But if the precision is off target, it can create other problems than variation. It is, therefore, important that the processes also are accurate to have the most optimal situation.
When identifying variances, there are two kinds of variances to identify: Common Causes and Special Causes. Common causes occur randomly and can be difficult to identify. Usually, a common cause doesn’t have an extreme impact on the output and will often be within three standard deviations (99,7%) from the mean. On the other hand, special causes occur out of special events such as a power cut or other external factors. These events are easy to identify but can be very difficult to control.
When analyzing variances between groups. Analysis of variation (ANOVA) can be very useful as it is a statistical method separating the total observed variation and estimating the magnitude of the variation that can be attributed to each source[10]. ANOVA can thus be applied to quantify effects of variation between relevant data groups – This is a useful tool for identifying and visualizing causes of variation between groups, which consequently can be eliminated.
Change processes and remove waste
When changing processes and eliminating waste it is important to first get the changes examined and verified by management and key stakeholders to ensure that the newly proposed flow is optimal in practice for the company and not just theoretically. Lastly, a new process overview must be created to visualize the optimized processes. It is also important to have in mind, that the main goal of removing waste and variability is to create more efficient processes. Therefore, it is important to understand common process families, as well as the overall process flow found in the first step ‘Understand process’. This is to ensure that removing waste and/or variability in one place won't have a negative effect on another place in the flow.
Actions / Tips & Tricks
- When using TIMWOOD, it is important to quantify the waste
- Value Stream Mapping is useful to get an overview of processes together with identifying waste
- When creating your VSM, use the Triangulation Spot method mentioned in the article ‘Identify and Understand your Processes’
- First focus on controlling common causes variances before looking at special causes
Series of articles on process improvements
This is the sixth article in the series of ten.
- Potential Impact when Changing Processes
- Why Companies Should Focus on Optimizing Company Processes
- Roadmap on Redesigning a Company’s Processes to Enhance Competitiveness
Step 1 Identify and Understand your Processes
Step 2 Monitor your Processes
Step 3 Identifying Waste and Variability in your Processes
Step 4 Become Resilient to Sudden Changes
Step 5 Simulate your New Process Design
Step 6 Implementation and Continuous Improvement Process
The next article ‘Become Resilient to Sudden Changes’ describes what to consider when building a robust process which is resilient to sudden changes
[1] Benson, R. and Kulkarni, N. S. (2011). Understanding Operational Waste from a Lean Biopharmaceutical Perspective. Pharmaceutical Engineering.
[2] Steiner, S. H. and Mackay, R. J. (2005). Statistical Engineering – An Algorithm for Reducing Variation in Manufacturing Process. ASQ Quality Press.
[3] Womack, J. P. and Jones, D. T. (2003). Lean Thinking: Banish Waste and Create Wealth in your Organization. First Free Press Edition.
[4] Elnamrouty, K. A. (2013). Seven Wastes Elimination Targeted by Lean Manufacturing Case Study. International Journal of Economics Finance and Management Science
[5] Zahraee, S. M. (2016). A survey on lean manufacturing implementation in a selected manufacturing industry in Iran. International Journal of Lean Six Sigma.
[6] Sandesh, A. S. and Pawan, C. H. (2014). First Pass Yield Improvement by Eliminating Base Plug Leakage in Feed Pump Manufacturing. International Journal of Science and Research.



